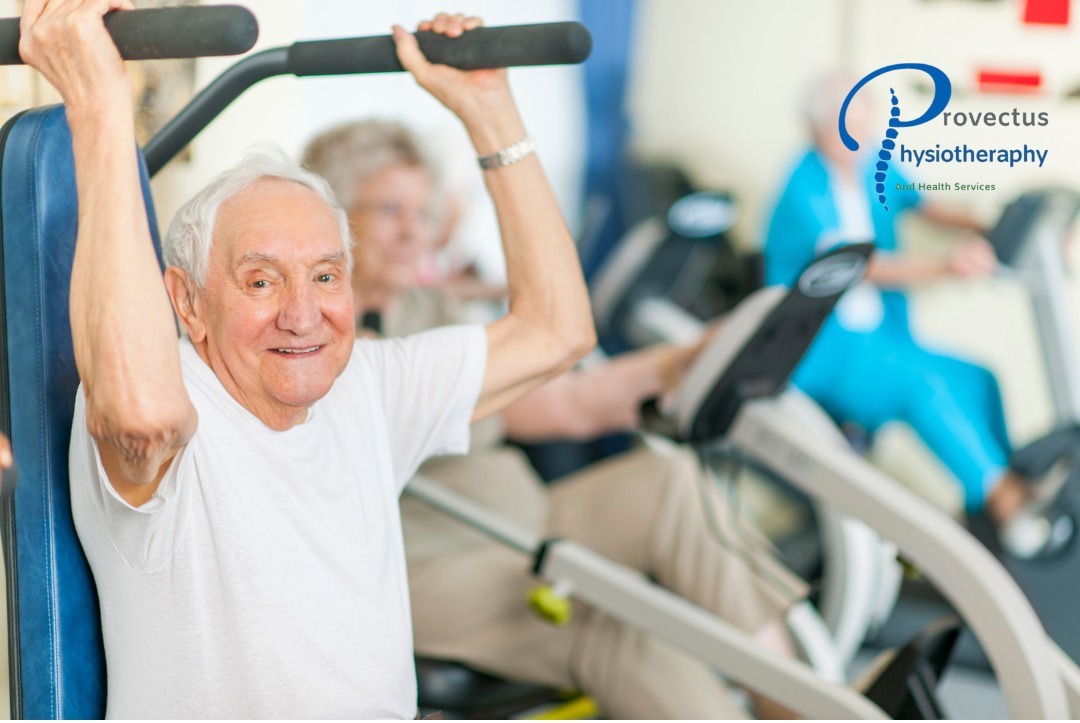
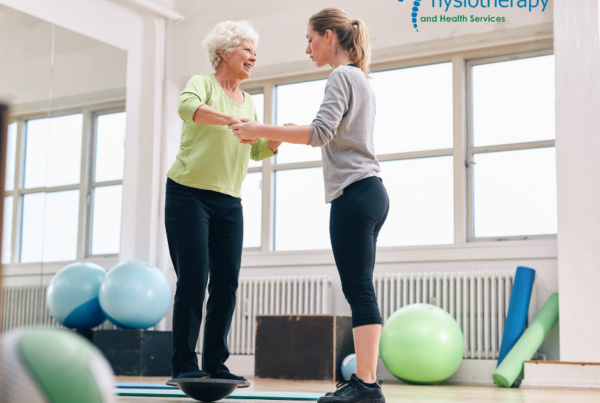
As we age, maintaining physical health becomes increasingly important. Regular physical activity has been shown to offer numerous health benefits for elderly individuals, from improved physical functioning and psychological well-being to enhanced cognitive performance. This blog post will explore the impact of regular exercise on the health of older adults, drawing insights from recent research.
Physical Health Benefits
1. Improved Cardiovascular Health
Regular physical activity significantly improves cardiovascular health in older adults. Paterson and Warburton (2010) found that exercise interventions lead to enhanced cardiovascular fitness, reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases, and overall improved health outcomes for older adults (1).
2. Enhanced Muscle Strength and Mobility
Exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining and improving muscle strength and mobility, which are essential for daily activities and preventing falls. Gómez-Cabello, Vicente-Rodríguez, and Vila-Maldonado (2013) noted that regular physical activity helps to preserve muscle mass, strength, and functional ability, thereby reducing the risk of falls and improving overall mobility (2).
3. Bone Health
Weight-bearing and resistance exercises are particularly beneficial for bone health, helping to prevent osteoporosis and fractures. The review by Chodzko-Zajko et al. (2009) highlighted that regular exercise enhances bone density and reduces the risk of osteoporosis in older adults (3).
Psychological and Cognitive Benefits
1. Psychological Well-being
Exercise has a profound impact on mental health, helping to alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. Chodzko-Zajko et al. (2009) emphasized that physical activity leads to improvements in mood, reduced symptoms of depression, and overall better psychological well-being in older adults (3).
2. Cognitive Functioning
Physical activity is also beneficial for cognitive health. Smith, Blumenthal, and Hoffman (2010) conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis that found regular exercise significantly enhances cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and executive functions, in healthy older adults (4).
Conclusion
Regular physical activity offers a myriad of benefits for older adults, including improved cardiovascular health, enhanced muscle strength and mobility, better bone health, and significant psychological and cognitive benefits. Incorporating regular exercise into daily routines can help elderly individuals maintain independence, improve their quality of life, and reduce the risk of various health conditions associated with aging. Encouraging older adults to stay active is essential for promoting health and well-being in this growing population segment.
References:
1. Paterson, D. H., & Warburton, D. E. R. (2010). The effectiveness of exercise interventions for older adults: A systematic review and meta analysis. Age and Ageing, 39(5), 662-672.
2. Gómez-Cabello, A., Vicente-Rodríguez, G., & Vila-Maldonado, S. (2013). The effects of regular physical activity on health in elderly patients: A review. Maturitas, 74(2), 109-114.
3. Chodzko-Zajko, W. J., Proctor, D. N., & Fiatarone Singh, M. A. (2009). Effects of exercise on physical functioning, physical health, and psychological well-being in older adults. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A, 64(3), 331-339.
4. Smith, P. J., Blumenthal, J. A., & Hoffman, B. M. (2010). The impact of exercise on cognitive functioning in healthy older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Research Reviews, 9(3), 285-300.